Recognizing the Early Indicators of an Underactive Thyroid
Understanding the Basics of an Underactive Thyroid
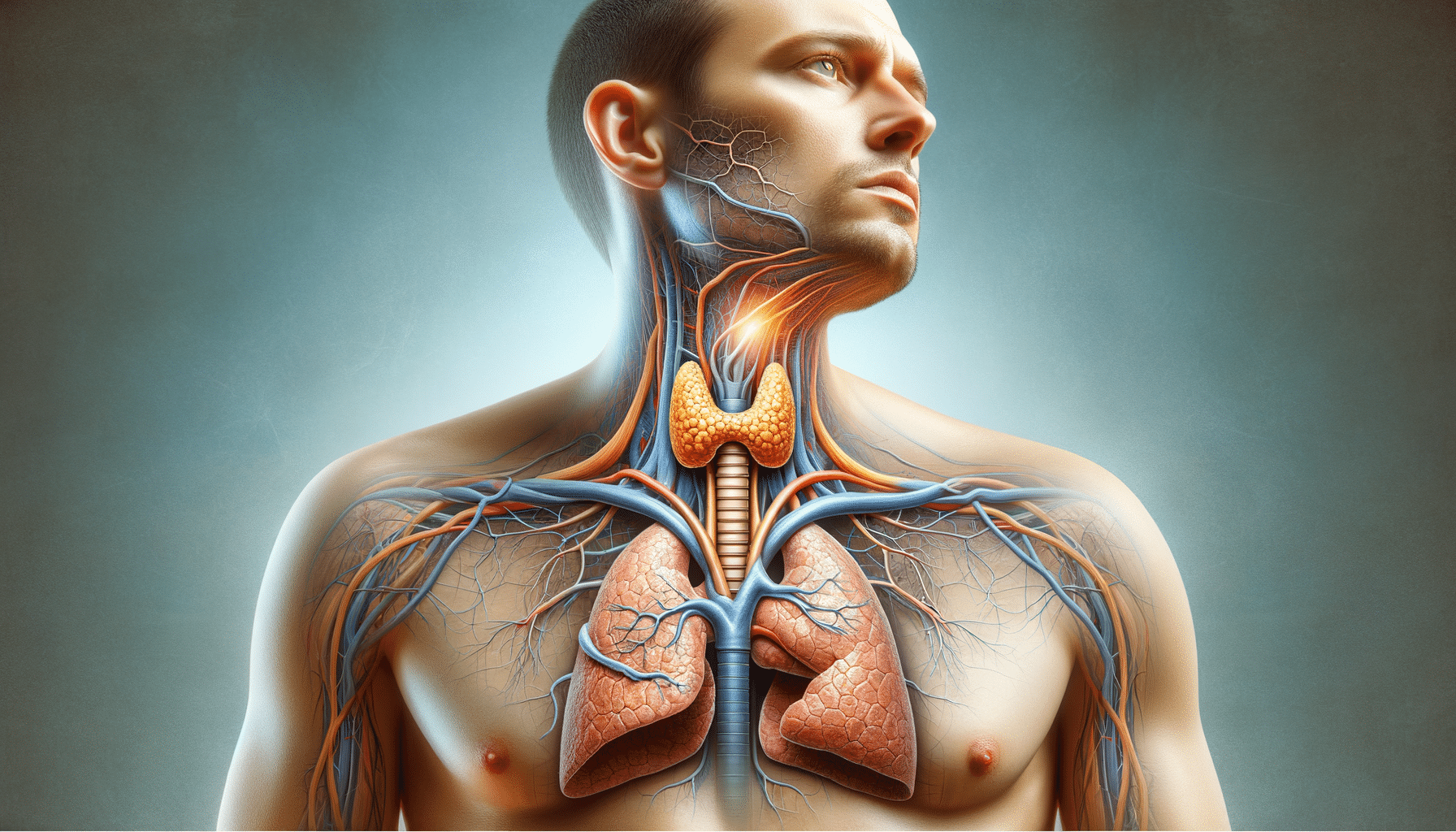
The thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped organ located at the base of the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating the body’s metabolism through the release of hormones. When the thyroid is underactive, a condition known as hypothyroidism, it fails to produce sufficient hormones, leading to a slowdown in metabolic processes. This can affect various bodily functions, manifesting in diverse symptoms that can gradually develop over time.
Hypothyroidism can be caused by several factors, including autoimmune diseases such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, surgical removal of the thyroid, radiation therapy, or certain medications. Understanding these underlying causes is essential for managing the condition effectively. The prevalence of hypothyroidism varies globally, but it is notably more common in women and older adults.
Recognizing an underactive thyroid early is crucial because untreated hypothyroidism can lead to severe health complications. These include heart problems, mental health issues, and peripheral neuropathy. By identifying symptoms early, individuals can seek medical advice and begin appropriate treatment, which typically involves hormone replacement therapy.
Common Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism can present with a variety of symptoms, which often develop slowly over time. This gradual onset can make it challenging to pinpoint the condition early. Common symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, and sensitivity to cold. These are often the first signs that prompt individuals to seek medical attention.
Beyond these initial symptoms, individuals may experience dry skin, constipation, and muscle weakness. The skin might become rough and pale, while the hair may thin or become brittle. Additionally, some people report experiencing joint pain or stiffness, which can impact daily activities.
Another significant symptom is depression or a general sense of feeling down. This can be accompanied by memory problems or difficulty concentrating, which are often mistaken for normal aging processes. Recognizing these symptoms as potential indicators of hypothyroidism is vital for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Impact on Daily Life and Well-being
The symptoms of an underactive thyroid can significantly affect an individual’s quality of life. Fatigue, for instance, can lead to decreased productivity at work or school and may affect personal relationships. The constant feeling of tiredness can also discourage physical activity, contributing to weight gain and exacerbating the condition’s symptoms.
Emotional well-being is another area impacted by hypothyroidism. The mood changes and depression associated with the condition can lead to social withdrawal and affect interpersonal relationships. This emotional toll can be challenging, especially when symptoms are misunderstood or dismissed by others.
Furthermore, the physical symptoms such as dry skin and hair loss can affect self-esteem and body image. People with hypothyroidism may find themselves spending more time managing these symptoms, which can be frustrating and time-consuming. Understanding the broader impact of hypothyroidism on daily life highlights the importance of early diagnosis and effective management.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosing hypothyroidism typically involves a combination of a physical examination, medical history review, and blood tests. The most common test measures the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) in the blood. Elevated TSH levels often indicate an underactive thyroid, as the body tries to stimulate more hormone production.
Once diagnosed, the primary treatment for hypothyroidism is hormone replacement therapy. This involves taking synthetic thyroid hormones to restore normal hormone levels. The dosage is tailored to the individual’s needs and requires regular monitoring to ensure effectiveness and avoid side effects.
In addition to medication, lifestyle changes can support treatment. A balanced diet rich in iodine, selenium, and zinc can aid thyroid function. Regular exercise can help manage weight and improve mood, while stress management techniques such as yoga or meditation can enhance overall well-being.
Living with Hypothyroidism: Tips and Strategies
Managing hypothyroidism effectively involves more than just medication. Incorporating lifestyle changes can significantly enhance quality of life. Here are some strategies that might help:
- Regular Check-ups: Consistent monitoring of thyroid levels is essential. Regular visits to a healthcare provider can help adjust medication as needed and ensure symptoms are managed effectively.
- Balanced Nutrition: Eating a diet that supports thyroid health is crucial. Foods rich in iodine, such as seafood, and those containing selenium and zinc, like nuts and seeds, can be beneficial.
- Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help combat fatigue and improve mood. Activities like walking, swimming, or yoga can be particularly beneficial.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate symptoms, so incorporating relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or mindfulness can be helpful.
By adopting these strategies, individuals with hypothyroidism can lead fulfilling lives. Education about the condition and open communication with healthcare providers also play a vital role in effective management.