What to Know Before Searching for a Tornado Shelter
Introduction to Tornado Shelters
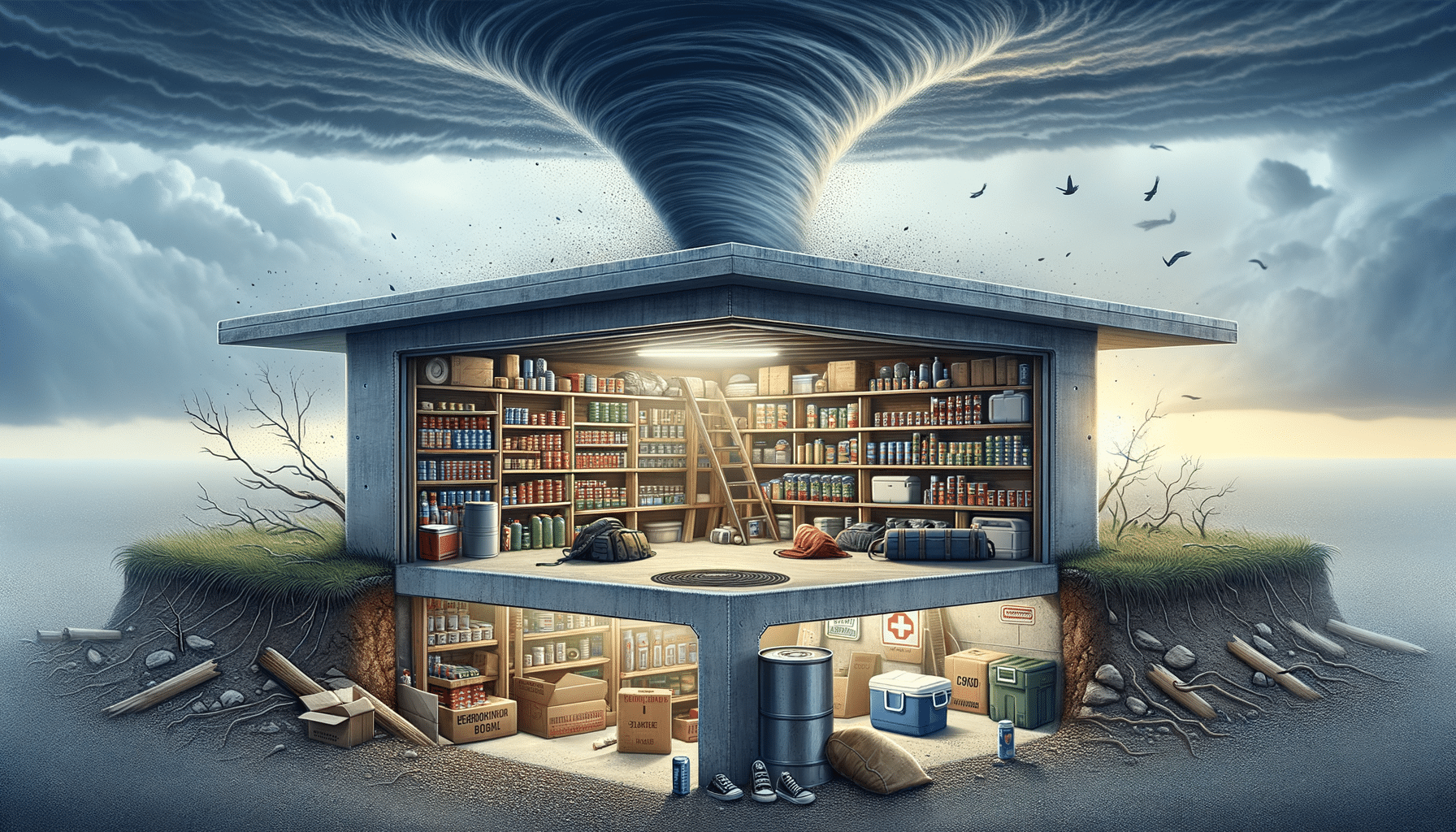
When severe weather strikes, having a safe place to take refuge is crucial. Tornado shelters are specifically designed to offer protection during such extreme conditions. These shelters can be lifesaving, providing a secure environment away from the dangers of high winds and flying debris. The importance of selecting the right tornado shelter cannot be overstated, as it can significantly impact the safety and well-being of you and your loved ones.
Understanding the different types of tornado shelters, their construction materials, and their locations can help individuals make informed choices. Whether you are considering installing a shelter at home or using a community facility, knowing what to look for can make all the difference when evaluating available options.
Types of Tornado Shelters
Tornado shelters come in various forms, each with unique features and benefits. The primary types include above-ground and underground shelters. Above-ground shelters, often made from steel or reinforced concrete, are designed to withstand high winds and debris. These shelters are typically installed in garages or other accessible areas within a home.
Underground shelters, on the other hand, offer protection by being below the surface, making them less susceptible to wind damage. They can be installed in basements or backyards and are often constructed from concrete or fiberglass. The choice between above-ground and underground shelters often depends on personal preference, budget, and the specific risks associated with the geographic location.
Materials Used in Tornado Shelters
The materials used in constructing tornado shelters play a vital role in their effectiveness. Common materials include steel, concrete, and fiberglass, each offering different levels of protection and durability. Concrete structures are renowned for their strength and ability to withstand extreme conditions, making them a popular choice for both above-ground and underground shelters.
Steel shelters, often prefabricated, provide a robust option that can be installed quickly and efficiently. Fiberglass shelters, while lightweight, offer excellent durability and are resistant to rust and corrosion. When choosing a material, consider factors such as longevity, maintenance, and the specific threats typical to your area.
Location and Accessibility
The location of a tornado shelter is crucial for ensuring quick and easy access during an emergency. Ideally, shelters should be placed in a location that is easily reachable from all parts of the home. For above-ground shelters, garages or interior rooms are common locations, while underground shelters might be installed in basements or backyards.
Accessibility is another important factor. Shelters should be designed to accommodate all household members, including those with mobility challenges. Features such as ramps, wide doorways, and adequate lighting can enhance accessibility and ensure that everyone can reach safety swiftly when needed.
Evaluating Available Options
When evaluating tornado shelters, several considerations come into play. First, assess the specific risks and weather patterns in your area. This information can guide you in choosing between above-ground and underground options. Consider the size of the shelter, ensuring it can comfortably accommodate your family and any pets.
Additionally, check for compliance with relevant safety standards and certifications. Many shelters are tested and certified to withstand specific wind speeds, providing peace of mind that they will perform as expected during a tornado. Finally, consider the cost and any potential financing options available to make the shelter an affordable addition to your home.