Early Colon Health and Treatment Plans
Understanding the First Warning Signs of Colon Cancer
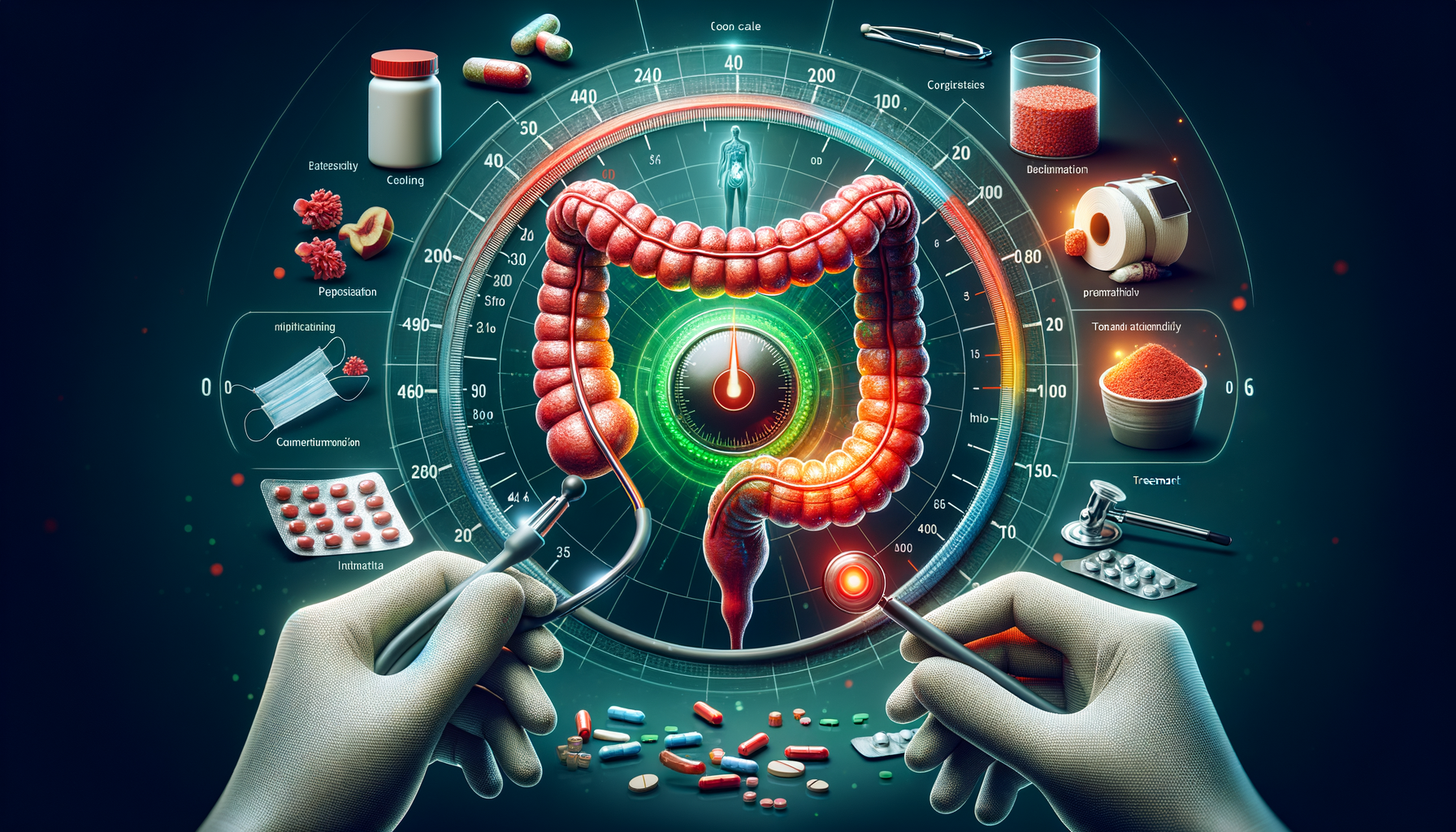
Colon cancer, a formidable health challenge, often begins with subtle symptoms that can easily be overlooked. Recognizing these early warning signs is crucial for timely intervention. The most common indicators include changes in bowel habits, such as persistent diarrhea or constipation, and a noticeable change in stool consistency. Additionally, rectal bleeding or blood in the stool can be alarming signals that warrant immediate medical attention. Unexplained weight loss and persistent abdominal discomfort, such as cramps or gas, are also notable symptoms.
While these symptoms can be associated with other less serious conditions, their persistence is a red flag. According to the American Cancer Society, early detection significantly increases the chances of successful treatment. Therefore, it’s imperative to consult a healthcare professional if any of these symptoms are present for more than a few weeks. Early diagnosis can lead to less invasive treatment options and a better prognosis.
It is also worth noting that some individuals may not experience any symptoms in the early stages of colon cancer, making regular screenings vital, especially for those over the age of 50 or with a family history of the disease. These screenings can detect precancerous polyps, which can be removed before they develop into cancer.
Diagnostic Procedures for Colon Cancer
Once symptoms suggest the possibility of colon cancer, several diagnostic procedures can confirm the diagnosis. The most common and effective method is a colonoscopy. This procedure involves the use of a long, flexible tube equipped with a camera to examine the entire colon and rectum. It allows for the detection and removal of polyps, which are then analyzed for cancerous cells. A colonoscopy is highly recommended as it can prevent cancer by removing polyps before they become malignant.
In addition to colonoscopy, other imaging tests such as CT colonography (also known as virtual colonoscopy) and flexible sigmoidoscopy may be used. These methods provide detailed images of the colon and can identify abnormalities. While less invasive, they may not offer the same level of detail as a traditional colonoscopy.
For patients unable to undergo these procedures, stool-based tests like the fecal immunochemical test (FIT) or the guaiac-based fecal occult blood test (gFOBT) can be alternatives. These tests detect hidden blood in the stool, which can be an early sign of cancer. However, positive results from these tests usually require follow-up with a colonoscopy.
Treatment Options for Colon Cancer
Treatment for colon cancer depends on the stage and location of the cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health. Surgery is often the primary treatment for early-stage colon cancer. During surgery, the cancerous section of the colon is removed, along with nearby lymph nodes. This can often lead to a cure if the cancer has not spread beyond the colon.
For more advanced stages, additional treatments such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy may be required. Chemotherapy uses drugs to destroy cancer cells and is typically used after surgery to eliminate any remaining cancerous cells. Radiation therapy, which uses high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells, is often used in conjunction with chemotherapy to improve outcomes.
Targeted therapy is another option, particularly for advanced colon cancer. This treatment involves drugs that specifically target cancer cell growth and division. Unlike traditional chemotherapy, targeted therapy can be more effective and have fewer side effects.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Changes
Prevention is a powerful tool in the fight against colon cancer. Several lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of developing this disease. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and low in red and processed meats, is recommended. These foods provide essential nutrients and fiber, which are beneficial for colon health.
Regular physical activity is also crucial. Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce cancer risk. Avoiding tobacco and limiting alcohol consumption are additional preventive measures that can further decrease risk.
Regular screenings are paramount, especially for individuals over 50 or those with a family history of colon cancer. Early detection through screenings like colonoscopies can prevent the development of cancer by identifying and removing precancerous polyps.
Conclusion: Taking Charge of Your Colon Health
Understanding the early warning signs of colon cancer and the available treatment options is essential for effective management and prevention. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing colon cancer. Regular screenings, a healthy lifestyle, and prompt attention to symptoms can make a substantial difference in outcomes.
For those diagnosed with colon cancer, a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and lifestyle adjustments offers a comprehensive approach to treatment. By working closely with healthcare professionals, patients can tailor their treatment plans to achieve the best possible results.
Ultimately, awareness and early intervention are key. By prioritizing colon health and taking preventive measures, individuals can lead healthier lives and improve their chances of overcoming colon cancer.