Understanding the Causes of Concrete Cracks
Concrete, though renowned for its strength and durability, is not immune to cracking. Understanding the causes of these cracks is the first step in addressing them effectively. Cracks in concrete can occur due to various reasons, such as thermal expansion and contraction, shrinkage during the curing process, and external loads. Thermal expansion and contraction are natural processes that occur as temperatures fluctuate. Concrete expands when warm and contracts when cool, potentially leading to cracks if proper joints are not in place. Shrinkage, on the other hand, happens as concrete dries and loses moisture, which can cause the surface to crack if it dries too quickly. Additionally, external loads such as heavy traffic or structural shifts can exert pressure on concrete, leading to stress and eventual cracking.
To effectively repair concrete cracks, it is crucial to identify the underlying cause. This involves examining the crack’s pattern, location, and size. For instance, hairline cracks might indicate surface shrinkage, while larger, deeper cracks could suggest structural issues. Understanding these nuances helps in selecting the appropriate repair method, ensuring that the repair is not only cosmetic but also addresses the root cause, preventing future damage.
Assessing the Severity of Concrete Cracks
Once the cause of the cracks is understood, the next step is to assess their severity. Not all cracks require immediate repair, but some can indicate significant structural problems that need urgent attention. Cracks are generally categorized based on their width and depth. Hairline cracks, often less than 0.1 mm wide, are typically superficial and not a major concern. However, wider cracks, especially those exceeding 6 mm, may indicate underlying structural issues.
Assessing the severity involves measuring the crack width and depth, as well as monitoring them over time to see if they are expanding. This can be done using simple tools such as crack gauges or more advanced methods like digital monitoring systems. It’s also important to consider the location of the crack. Cracks in load-bearing structures or those that affect the integrity of the building should be addressed promptly. By accurately assessing the severity, one can prioritize repairs and allocate resources effectively, ensuring that critical issues are resolved before they escalate.
Choosing the Right Repair Method
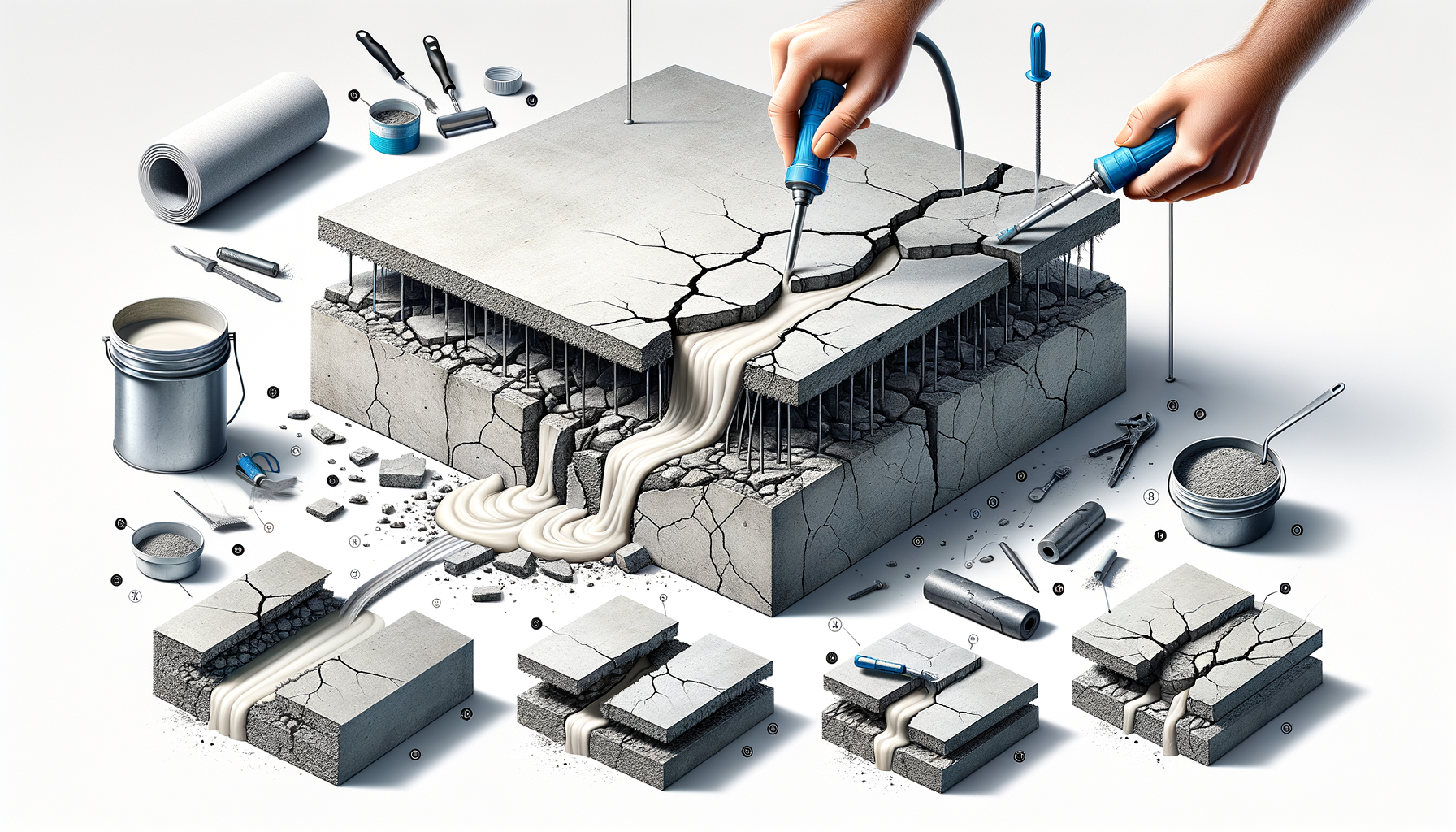
After identifying the cause and assessing the severity, selecting the appropriate repair method is crucial. Various techniques are available, each suited to different types of cracks and their causes. Common methods include epoxy injections, routing and sealing, and stitching. Epoxy injections are ideal for structural cracks as they restore the original strength of the concrete. This method involves injecting a two-part epoxy resin into the crack, which bonds with the concrete and hardens into a solid mass.
For non-structural cracks, routing and sealing is a popular choice. This involves enlarging the crack along its exposed face and filling it with a sealant, which prevents water infiltration and further deterioration. Stitching, on the other hand, involves drilling holes on both sides of the crack and installing metal stitches to hold the sides together. This method is particularly effective for controlling movement in active cracks.
The choice of method depends on factors such as the crack’s location, size, and function of the concrete structure. By selecting the right repair technique, one can ensure the longevity and durability of the repair, preventing future issues.
Materials for Effective Concrete Crack Repair
The choice of materials plays a pivotal role in the success of concrete crack repairs. Different materials are suited for different repair methods and types of cracks. Epoxy resins are commonly used for structural repairs due to their high strength and bonding capabilities. These resins are designed to penetrate deep into the crack, providing a durable and lasting solution.
For sealing surface cracks, polyurethane sealants are often preferred. These sealants are flexible and can accommodate slight movements in the concrete, making them ideal for non-structural repairs. Additionally, they are resistant to moisture and chemicals, providing protection against further damage.
In some cases, cementitious repair mortars are used, especially for larger cracks or when restoring the surface appearance is important. These mortars are designed to bond well with the existing concrete and can be colored to match the surrounding area. By selecting the appropriate materials, one can ensure that the repair is not only effective but also aesthetically pleasing, maintaining the integrity and appearance of the structure.
Preventive Measures to Avoid Future Cracks
While repairing existing cracks is essential, preventing future cracks is equally important. Implementing preventive measures can save time and resources in the long run. One effective strategy is to ensure proper curing of concrete during construction. This involves maintaining adequate moisture levels and temperature conditions to prevent shrinkage cracks.
Additionally, incorporating control joints in concrete structures can help manage thermal expansion and contraction. These joints allow the concrete to expand and contract without causing random cracking. Regular maintenance and inspection of concrete structures can also help identify potential issues early, allowing for timely intervention.
Another preventive measure is to address any drainage issues around the concrete structure. Poor drainage can lead to water accumulation, which can weaken the concrete and lead to cracking. By ensuring proper drainage, one can protect the concrete from water-related damage.
By taking these preventive steps, one can enhance the durability and longevity of concrete structures, minimizing the likelihood of future cracks and the need for repairs.



Leave a Reply