Recognizing the Early Indicators of an Underactive Thyroid
Understanding the Thyroid and Its Role
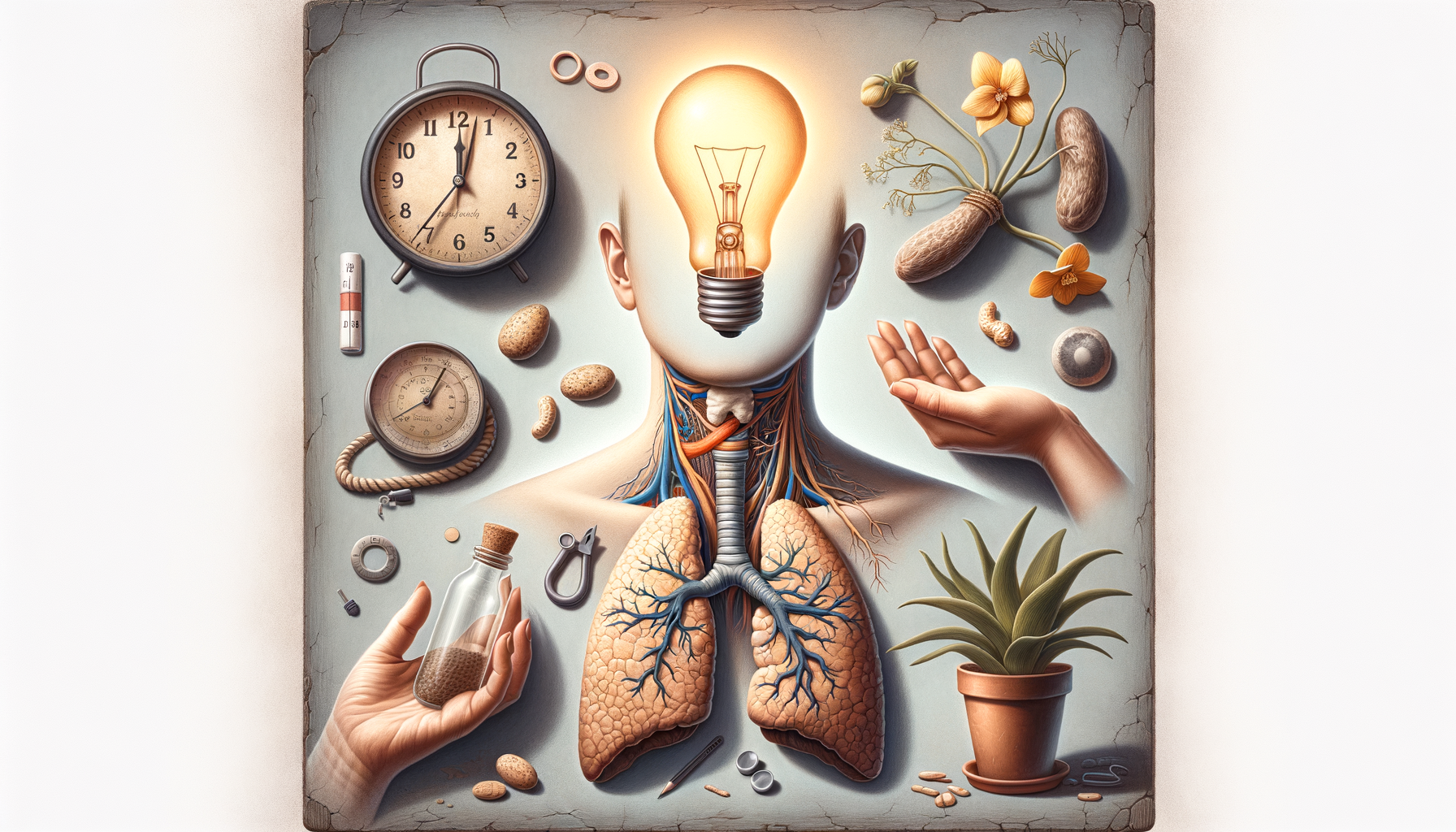
The thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped organ located at the base of the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating the body’s metabolism. It produces hormones like thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which influence every cell in the body. These hormones control how fast or slow the cells work, affecting metabolism, heart rate, and even body temperature. When the thyroid is underactive, a condition known as hypothyroidism, it doesn’t produce enough hormones, leading to a slowdown in bodily functions.
Hypothyroidism can be caused by several factors, including autoimmune diseases like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, certain medications, radiation therapy, and even iodine deficiency. Understanding the thyroid’s function helps in recognizing how its dysfunction can lead to various health issues. The subtlety of the symptoms often makes it difficult to diagnose early, which is why awareness is key.
Common Symptoms of an Underactive Thyroid
Hypothyroidism can manifest through a range of symptoms, many of which might be mistaken for other health issues. Some common signs include:
- Fatigue: A persistent feeling of tiredness or lack of energy is one of the most prevalent symptoms.
- Weight Gain: Unexplained weight gain or difficulty losing weight can be a sign of a sluggish metabolism.
- Cold Sensitivity: An underactive thyroid can make individuals more sensitive to cold temperatures.
- Dry Skin and Hair: The skin may become dry and rough, and hair may become brittle or fall out.
- Mood Changes: Depression or mood swings can occur as a result of hormonal imbalances.
These symptoms can vary greatly in intensity and may develop gradually, making it crucial to pay attention to changes in health and consult with a healthcare provider if multiple symptoms are present.
Impact on Daily Life and Well-being
The symptoms of an underactive thyroid can have a profound impact on an individual’s daily life. Fatigue and mood changes can affect work performance and personal relationships, while weight gain and physical discomfort may lead to decreased self-esteem and social withdrawal. The chronic nature of these symptoms can lead to a diminished quality of life if not addressed.
Moreover, untreated hypothyroidism can lead to more severe health complications over time, such as heart problems, infertility, and in extreme cases, myxedema coma, a life-threatening condition. Therefore, recognizing and addressing these symptoms early can prevent further health deterioration and improve overall well-being.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosing hypothyroidism typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and blood tests to measure levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and thyroid hormones. A higher TSH level with low thyroid hormone levels often indicates an underactive thyroid.
Treatment usually involves daily use of synthetic thyroid hormone levothyroxine, which restores adequate hormone levels, reversing the signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism. Regular monitoring and blood tests are essential to ensure the dosage is correct. Lifestyle changes, such as a balanced diet rich in iodine and regular exercise, can also support thyroid health.
It’s important for individuals to work closely with their healthcare providers to manage their condition effectively, as treatment needs may change over time.
Living with Hypothyroidism: Tips and Advice
Living with an underactive thyroid requires ongoing management and lifestyle adjustments. Here are some tips to help manage the condition:
- Medication Adherence: Take thyroid medication consistently as prescribed, ideally at the same time each day.
- Dietary Considerations: Incorporate foods rich in iodine and selenium, such as fish, dairy, and nuts, to support thyroid function.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to boost metabolism and improve energy levels.
- Stress Management: Practice stress-reducing techniques like yoga or meditation to help manage mood changes.
- Regular Check-ups: Schedule regular visits with a healthcare provider to monitor thyroid levels and adjust treatment as necessary.
By taking proactive steps and remaining informed about their condition, individuals with hypothyroidism can lead healthy, fulfilling lives.