Understanding Stroke: A Medical Overview
Strokes are a serious medical condition that occurs when the blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, preventing brain tissue from getting oxygen and nutrients. This can lead to brain cells starting to die within minutes. Understanding the mechanisms of a stroke is crucial for recognizing its symptoms and seeking timely medical intervention. There are two main types of strokes: ischemic and hemorrhagic. Ischemic strokes, the most common type, are caused by blockages or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to the brain, often due to blood clots or fatty deposits. Hemorrhagic strokes occur when a blood vessel in the brain bursts, leading to bleeding in or around the brain.
Risk factors for stroke include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, high cholesterol, and a family history of stroke. Lifestyle factors such as a sedentary lifestyle, unhealthy diet, and excessive alcohol consumption also contribute to the risk. Recognizing these risk factors and managing them through lifestyle changes and medical interventions can significantly reduce the risk of stroke.
Recognizing the Symptoms of a Stroke
Recognizing the symptoms of a stroke is crucial for ensuring prompt medical attention, which can significantly improve outcomes. The acronym FAST is a helpful tool for remembering the major warning signs of a stroke:
- Face drooping: One side of the face may droop or feel numb. Ask the person to smile, and see if the smile is uneven.
- Arm weakness: One arm may be weak or numb. Ask the person to raise both arms. Does one arm drift downward?
- Speech difficulty: Speech may be slurred or hard to understand. Ask the person to repeat a simple sentence. Can they do it correctly?
- Time to call emergency services: If someone shows any of these symptoms, even if they go away, call emergency services immediately.
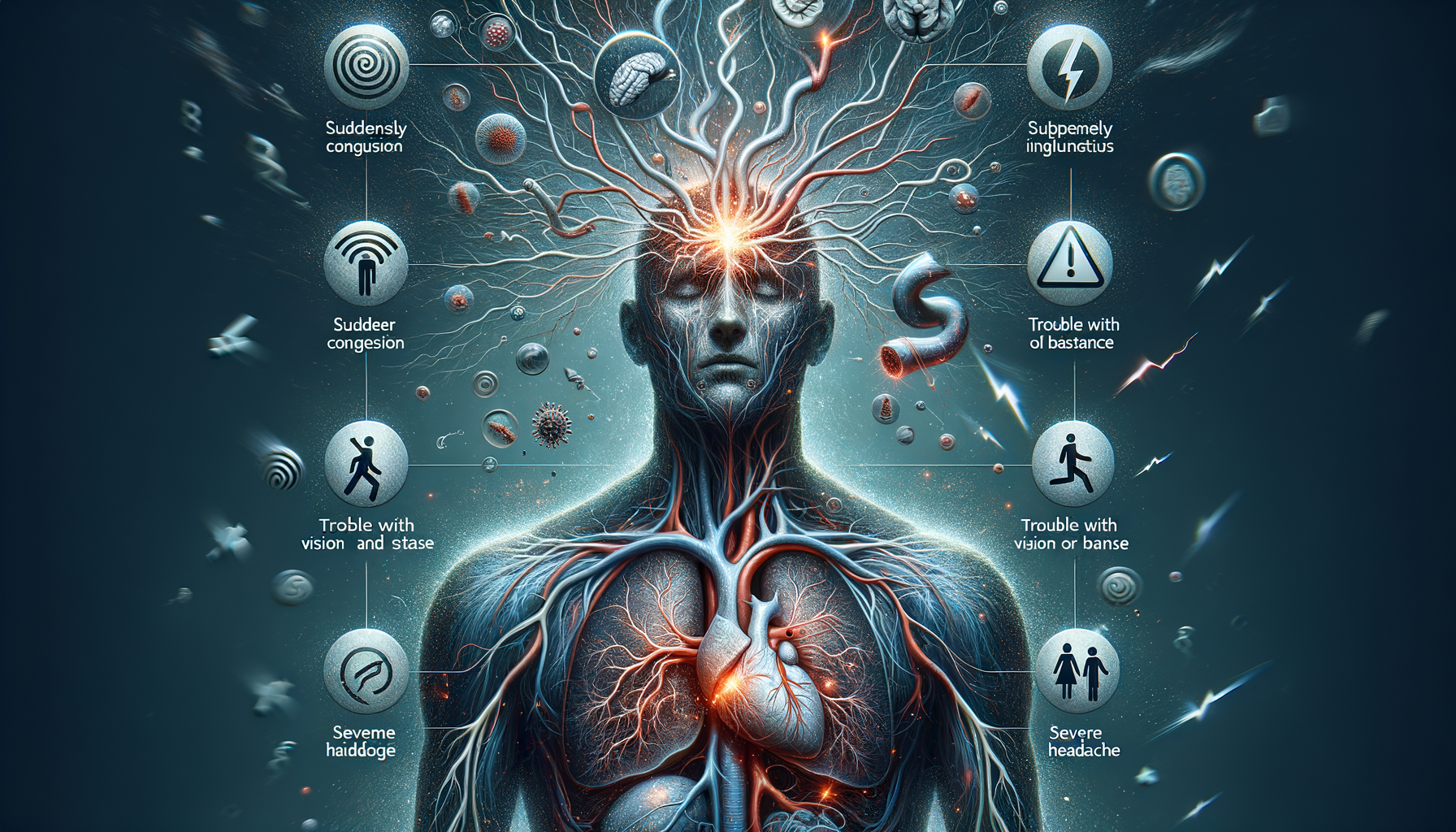
Additional symptoms may include sudden confusion, trouble seeing in one or both eyes, difficulty walking, dizziness, or a sudden severe headache with no known cause. These symptoms can vary in intensity and may occur suddenly, making it imperative to act quickly.
Factors Contributing to Stroke
Several factors can contribute to the likelihood of experiencing a stroke, many of which are related to lifestyle and health conditions. High blood pressure is the most significant controllable risk factor for stroke. It can damage blood vessels, making them more likely to clog or burst. Managing blood pressure through medication, diet, and regular exercise is vital.
Smoking is another major risk factor. Chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage blood vessels and lead to atherosclerosis, a condition where arteries become clogged with fatty substances. Quitting smoking reduces the risk of stroke significantly. Diabetes also increases the risk of stroke, as high blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels over time. Maintaining blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and medication is essential for reducing stroke risk.
Other factors include obesity, excessive alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle. Engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and limiting alcohol intake are effective strategies for reducing stroke risk.
Prevention and Management Strategies
Preventing a stroke involves addressing the risk factors that can lead to its occurrence. Regular medical check-ups to monitor blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar can help identify potential problems early. Medications may be prescribed to manage these conditions, and adherence to prescribed treatments is crucial.
Lifestyle modifications play a significant role in stroke prevention. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce cholesterol levels. Regular physical activity strengthens the heart and improves circulation, reducing the risk of stroke.
For those who have already experienced a stroke, rehabilitation and management are critical. Rehabilitation may include physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy to help regain lost functions and improve quality of life. Ongoing medical care and lifestyle adjustments are essential to prevent recurrent strokes.
Conclusion: Awareness and Action
Understanding the symptoms and causes of stroke is vital for both prevention and timely intervention. By recognizing the signs of a stroke and knowing the risk factors, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk and seek immediate medical help when necessary. Lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and smoking cessation, are powerful tools in stroke prevention. Moreover, managing underlying health conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes is crucial.
Ultimately, increasing awareness about stroke and its warning signs can lead to quicker responses and better outcomes. By staying informed and vigilant, individuals can protect themselves and their loved ones from the potentially devastating effects of a stroke.



Leave a Reply